Managing e-commerce data across multiple platforms becomes challenging as your WooCommerce store scales. Without proper data integration, you’re left manually exporting reports, struggling with fragmented analytics, and missing opportunities to make data-driven decisions. WooCommerce to BigQuery integration solves this by centralizing your store data in Google’s powerful cloud data warehouse, enabling advanced analytics, real-time reporting, and seamless data sharing across your organization.
This guide walks you through two proven methods to connect WooCommerce with BigQuery—manual CSV uploads and automated no-code tools—so you can choose the approach that fits your technical capabilities and business needs.
Summary
- Manual CSV Export Method: Export WooCommerce data as CSV files and upload them to BigQuery—ideal for one-time migrations or small datasets
- No-Code Integration Tools: Automate data syncing between WooCommerce and BigQuery without writing code—perfect for ongoing, real-time data updates
- Data Selection Strategy: Understand which WooCommerce datasets (orders, customers, products, inventory) provide the most value in BigQuery
- Implementation Steps: Follow detailed workflows for both manual and automated integration approaches
- Common Challenges: Learn how to troubleshoot data mapping errors, API rate limits, and schema mismatches
Method 1: Uploading WooCommerce Data to BigQuery Manually
Manual integration works well for one-time data migrations, historical analysis projects, or situations where you need full control over data transformation before upload. This approach requires no third-party tools but demands more hands-on effort.
Step 1: Export WooCommerce Data as CSV Files
WooCommerce stores critical business data across multiple tables in your WordPress database. Exporting this data requires either plugins or direct database access.
Using WooCommerce’s Native Export Feature:
- Navigate to WooCommerce → Reports in your WordPress dashboard
- Select the data type you want to export (Orders, Customers, or Products)
- Apply date range filters and any additional criteria
- Click “Export CSV” to download the file
Using Export Plugins for Advanced Control:
For more comprehensive data exports, consider plugins like “WP All Export” or “Advanced Order Export For WooCommerce”:
- Install and activate your chosen export plugin
- Configure custom field mappings to include all necessary data points
- Schedule exports or run them on demand
- Download the generated CSV files to your local system
Table 1: Key WooCommerce Data Tables to Export
| Data Type | Key Fields | Use Case in BigQuery |
| Orders | Order ID, Date, Total, Status, Customer ID | Revenue analysis, sales forecasting |
| Customers | Customer ID, Email, Registration Date, Total Spent | Segmentation, lifetime value calculation |
| Products | Product ID, SKU, Price, Stock Status, Category | Inventory optimization, pricing analysis |
| Order Items | Item ID, Product ID, Quantity, Line Total | Product performance, cross-sell analysis |
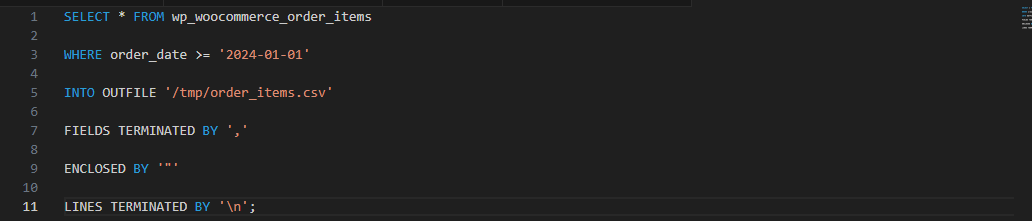
Direct Database Export (Advanced):
Technical users can export data directly from MySQL using phpMyAdmin or command-line tools:
Ensure your CSV files are properly formatted with clear column headers, consistent date formats (preferably ISO 8601), and UTF-8 encoding to prevent import errors.
Step 2: Import WooCommerce Data into BigQuery
Once you’ve exported your WooCommerce data, you can upload it to BigQuery through the Google Cloud Console.
Preparing Your BigQuery Environment:
- Log in to Google Cloud Console and select or create a project
- Navigate to BigQuery from the main menu
- Create a new dataset to house your WooCommerce data (e.g., “woocommerce_data”)
- Set the appropriate data location based on your compliance requirements
Uploading CSV Files:
- Within your dataset, click “Create Table.”
- Select “Upload” as the source type
- Choose your CSV file from your local system
- Name your table appropriately (e.g., “orders,” “customers,” “products”)
- Enable “Auto-detect” schema or manually define field types
Table 2: Recommended BigQuery Schema Settings for WooCommerce Data
| WooCommerce Field | BigQuery Data Type | Notes |
| Order Date | TIMESTAMP | Enables time-series analysis |
| Order Total | NUMERIC(10,2) | Preserves decimal precision |
| Customer Email | STRING | Use for joins with the customer table |
| Product SKU | STRING | Primary identifier for products |
| Quantity | INTEGER | Whole numbers only |
Schema Mapping Considerations:
BigQuery requires explicit data types, so pay attention to:
- Date and timestamp fields must follow ISO format or be converted
- Currency values should use the NUMERIC type to avoid floating-point errors
- Boolean fields from WooCommerce should map to the BOOLEAN type in BigQuery
- Text fields with potential special characters need a STRING type
After upload, verify your data integrity by running sample queries to check record counts, null values, and data type consistency.
Now that we’ve covered the manual approach, let’s explore how no-code tools can automate this entire process.
Step 3: Schedule Regular Manual Uploads
For ongoing data synchronization using the manual method, establish a consistent upload schedule:
- Set calendar reminders for weekly or monthly exports
- Create standardized naming conventions for your CSV files (e.g., “orders_2024_01.csv”)
- Document your export and upload procedures for team consistency
- Consider using Google Cloud Storage as an intermediary staging area for large files
While manual uploads provide control, they become time-consuming as data volume grows. This is where automated solutions deliver significant value.
Method 2: Using No-Code Tools to Sync WooCommerce Data with BigQuery
No-code integration platforms eliminate repetitive manual work by automatically syncing WooCommerce data to BigQuery on your chosen schedule. Tools like Zapier with WooCommerce extensions, Airbyte, Stitch Data, and Fivetran support WooCommerce BigQuery integration without requiring developer resources.
Step 1: Set Up WooCommerce as the Source
Choosing Your Integration Platform:
Popular no-code tools for WooCommerce BigQuery data sync include:
- Airbyte: Open-source, self-hosted option with an extensive connector library
- Stitch Data: Managed service with automatic schema mapping
- Fivetran: Enterprise-grade with advanced monitoring and alerts
- Zapier: User-friendly for simple workflows, but limited on data volume
Connecting Your WooCommerce Store:
- Sign up for your chosen integration platform and create a new connection
- Select WooCommerce as your data source
- Enter your store URL (e.g., “yourstore.com”)
- Generate and input API credentials from WooCommerce → Settings → Advanced → REST API
- Configure API permissions (typically “Read” access is sufficient)
Table 3: WooCommerce API Authentication Requirements
| Platform | Authentication Method | Required Permissions |
| Airbyte | Consumer Key + Secret | Read |
| Stitch Data | Consumer Key + Secret | Read |
| Fivetran | Consumer Key + Secret | Read |
| Custom Integration | OAuth 2.0 or Key/Secret | Read + Write (if bidirectional) |
Selecting Data Streams:
Most integration tools let you choose which WooCommerce data objects to sync:
- Orders: Essential for revenue tracking and sales analysis
- Customers: Enables cohort analysis and customer segmentation
- Products: Powers inventory analysis and product performance reporting
- Refunds: Critical for accurate revenue recognition
- Subscriptions: If using the WooCommerce Subscriptions extension
- Coupons: Tracks promotional campaign effectiveness
Enable only the data streams you need to optimize sync performance and reduce BigQuery storage costs. For most businesses, orders, customers, and products form the core dataset.
Step 2: Set Up BigQuery as the Destination
Configuring BigQuery Connection:
- In your integration tool, add BigQuery as the destination
- Authenticate using a Google Cloud service account with BigQuery permissions
- Select your existing BigQuery project or create a new one
- Choose or create a dataset specifically for WooCommerce data
Service Account Setup:
Create a Google Cloud service account with these permissions:
- BigQuery Data Editor
- BigQuery Job User
Download the JSON key file and upload it to your integration platform for authentication.
Data Sync Configuration:
Configure how your integration handles data updates:
Replication Methods:
- Full Refresh: Replaces all data in BigQuery with current WooCommerce data (simple but resource-intensive)
- Incremental Append: Adds only new records since last sync (efficient for growing datasets)
- Incremental Upsert: Updates existing records and adds new ones (best for maintaining data accuracy)
Choose incremental upsert for most scenarios to balance efficiency with accuracy, particularly for orders that might change status after initial creation.
Table 4: Sync Frequency Recommendations by Data Type
| Data Type | Recommended Frequency | Reasoning |
| Orders | Every 15-60 minutes | Enables near-real-time reporting |
| Customers | Daily | Changes less frequently |
| Products | Every 6-24 hours | Inventory updates occur regularly |
| Refunds | Hourly | Important for accurate revenue |
Data Transformation Options:
Many no-code tools offer basic transformation capabilities:
- Filter out test orders or draft products
- Rename fields to match your existing BigQuery schema
- Convert time zones to your business location
- Flatten nested JSON structures from WooCommerce API responses
For advanced transformations, consider using BigQuery views or scheduled queries after data lands in your warehouse.
Step 3: Monitor and Optimize Your Integration
Setting Up Monitoring:
- Enable email alerts for sync failures in your integration platform
- Create BigQuery scheduled queries to validate data freshness
- Monitor API rate limit consumption to avoid service disruptions
- Track BigQuery storage and query costs in Google Cloud Console
Common Optimization Strategies:
- Sync only modified records using WooCommerce’s “modified_after” filter
- Partition BigQuery tables by date for improved query performance
- Archive historical data older than 2-3 years to separate tables
- Use clustering on frequently filtered fields like order status or customer ID
If you’re looking to integrate other platforms with your e-commerce stack, check out our guide on Shopify to Google Sheets integration for similar automation strategies.
Comparing Manual vs. No-Code Integration Methods
Understanding when to use each approach helps you make the right choice for your business context.
When Manual Integration Makes Sense:
- One-time historical data migration for analysis projects
- Small datasets (under 10,000 records) updated infrequently
- High security requirements where API access is restricted
- Learning and experimentation phase before committing to automation
- Budget constraints are preventing paid integration tool subscriptions
When No-Code Tools Excel:
- Ongoing, regular data synchronization needs
- Large or rapidly growing datasets requiring frequent updates
- Teams without dedicated developer resources
- Need for real-time or near-real-time analytics
- Multiple data sources require centralized data warehousing
For businesses serious about data-driven decision-making, no-code tools typically provide better ROI despite the platform costs. The time savings, reduced error rates, and accessibility to non-technical team members justify the investment.
Advanced WooCommerce BigQuery Use Cases
Once your WooCommerce data flows into BigQuery, you unlock powerful analytics capabilities beyond basic reporting.
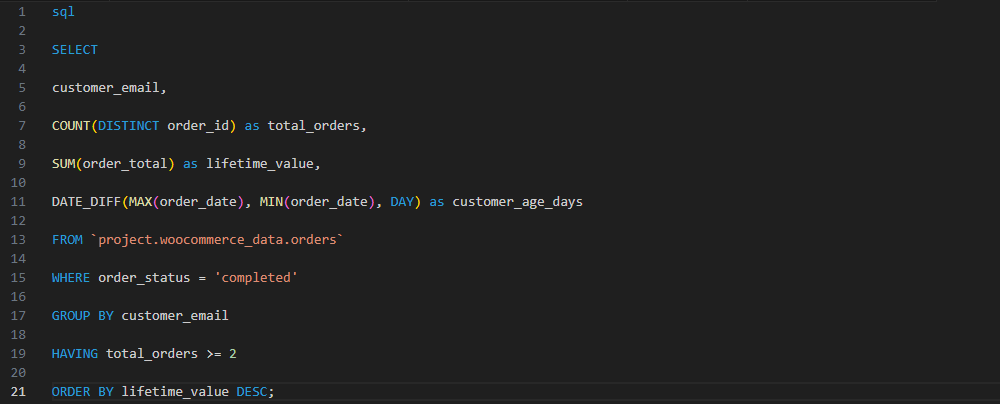
Customer Lifetime Value Analysis
Combine order history with customer data to calculate CLV segments:
This analysis helps identify your most valuable customers and predict future revenue potential.
Inventory Optimization
Join product, order, and inventory data to forecast stock needs:
- Calculate average daily sales velocity by product
- Identify seasonal trends impacting specific SKUs
- Flag slow-moving inventory consuming warehouse space
- Predict stockout risks based on current inventory and sales trends
Marketing Attribution
When combined with Google Analytics data in BigQuery, you can attribute revenue to specific marketing campaigns, channels, and customer touchpoints. Understanding which acquisition channels drive the highest CLV customers transforms marketing budget allocation.
For comprehensive e-commerce analytics strategies, explore our WooCommerce reporting and analytics guide.
Key Takeaways
- Choose the right integration method: Manual exports work for one-time needs; no-code tools excel for ongoing synchronization
- Start with core data streams: Focus on orders, customers, and products before expanding to additional datasets
- Implement incremental syncing: Use upsert or append modes to maintain data accuracy while optimizing performance
- Monitor continuously: Set up alerts and validate data freshness to catch issues early
- Leverage BigQuery’s power: Use SQL queries, scheduled reports, and visualization tools to extract actionable insights
Final Thoughts
Integrating WooCommerce with BigQuery transforms how you analyze and act on e-commerce data. Whether you choose manual CSV uploads for one-time projects or automated no-code tools for continuous synchronization, the key is matching your integration approach to your business needs, technical capabilities, and data volume.
The WooCommerce BigQuery integration enables advanced analytics, predictive modeling, and data-driven decision-making that aren’t possible with WooCommerce’s native reporting alone. As your store grows, this foundation scales with you, supporting increasingly sophisticated analysis without platform limitations.
Ready to take your WooCommerce analytics to the next level? Connect with our e-commerce integration specialists to discuss your specific requirements or leverage our WordPress development and WordPress ecommerce services to build a scalable, secure WooCommerce–BigQuery data integration that supports long-term growth.
FAQs
What Is WooCommerce to BigQuery Integration?
WooCommerce to BigQuery integration is the process of connecting your WooCommerce store to Google BigQuery, enabling automatic or manual data transfer for advanced analytics, reporting, and business intelligence.
Why Should I Connect WooCommerce with BigQuery?
Connecting WooCommerce with BigQuery centralizes your e-commerce data for advanced SQL queries, combines it with other business data sources, enables real-time reporting, and scales to handle growing data volumes without performance degradation.
What Data Can Be Sent From WooCommerce to BigQuery?
You can sync orders, customers, products, refunds, subscriptions, coupons, product categories, customer reviews, and custom fields. Most integrations support all core WooCommerce data objects through the REST API.
Can WooCommerce Data Be Synced With BigQuery in Real Time?
Yes, using no-code integration tools with frequent sync schedules (every 15-30 minutes), you can achieve near-real-time data synchronization. True real-time requires custom webhook implementations.
Is Coding Required to Integrate WooCommerce With BigQuery?
No, no-code integration platforms like Airbyte, Stitch Data, and Fivetran enable WooCommerce BigQuery data sync without programming. Manual CSV uploads also require no coding skills.
Are No-Code Tools Safe for WooCommerce BigQuery Integration?
Yes, reputable no-code platforms use secure API connections, encrypt data in transit and at rest, and comply with data protection regulations like GDPR. Always verify security certifications before selecting a tool.
How Often Should WooCommerce Data Be Updated in BigQuery?
Update frequency depends on your needs: orders benefit from hourly or more frequent syncs for near-real-time reporting, while customer and product data can update daily or weekly.
What Are the Common Challenges in WooCommerce to BigQuery Integration?
Common challenges include API rate limiting from WooCommerce, schema mismatches between WooCommerce and BigQuery data types, handling deleted records, managing large historical datasets, and maintaining sync consistency during WooCommerce updates.